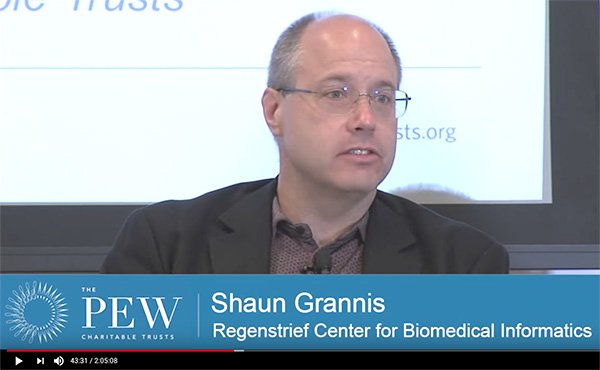
WASHINGTON, D.C. — Regenstrief Center for Biomedical Informatics Director Shaun Grannis, M.D., took part in a Pew Charitable Trust panel to discuss how to better match patients with their correct electronic health record and improve patient care.
Electronic health records allow care providers the ability to exchange individuals’ health data with their colleagues elsewhere. However, patients may not always be accurately matched to their records — a problem that can occur up to half the time when individuals seek care in multiple places.
Pew looked at research on several strategies to improve patient matching rates. The research was compiled and released in a report which examined the potential of biometrics and other unique identifiers, patient-empowered approaches, data standardization, and the use of data from third-party sources to address this problem. The Pew report found that standardizing data is likely to have the biggest impact.
Dr. Grannis reviewed the report and discussed its findings with a panel of experts in Washington, D.C. He talked about his work with the Indiana Health Information Exchange, where research found that standardizing address and last name actually had the biggest impact on match rates in Indiana.